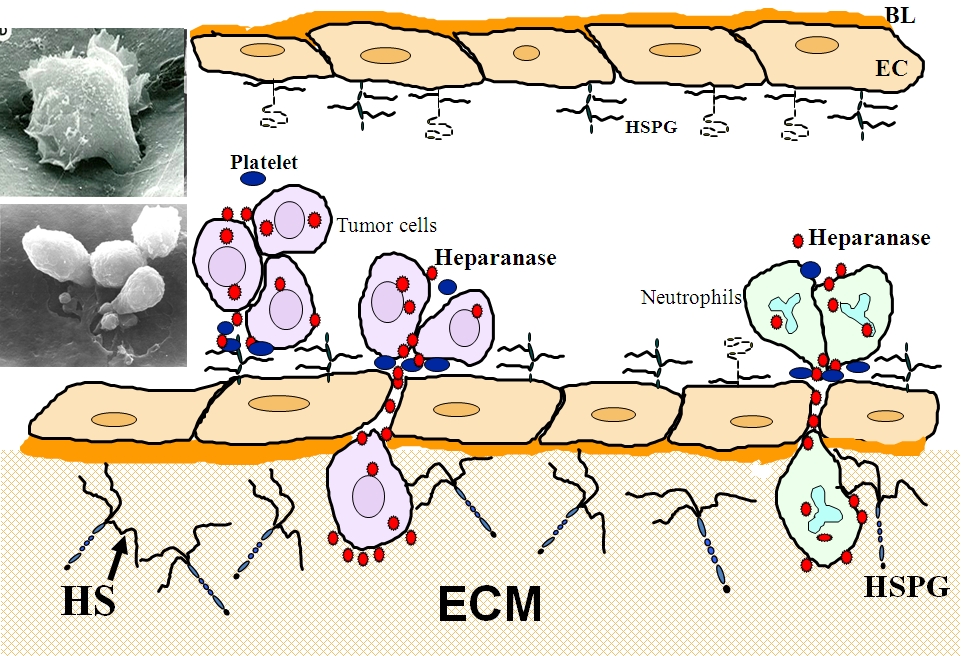
Figure 1.
Heparanase-mediated extravasation of blood-borne cells. Heparanase expressed by tumor cells (left) and neutrophils (right) promotes cell invasion in between adjacent vascular endothelial cells (EC) and through their underlying basal lamina (BL) into the extracellular matrix (ECM). Left: Scanning electron micrographs showing invasion of T lymphoma cells, in the absence (top) or presence (bottom) of platelets, through a monolayer of cultured vascular EC. HS, heparan sulfate; HSPG, heparan sulfate proteoglycan.