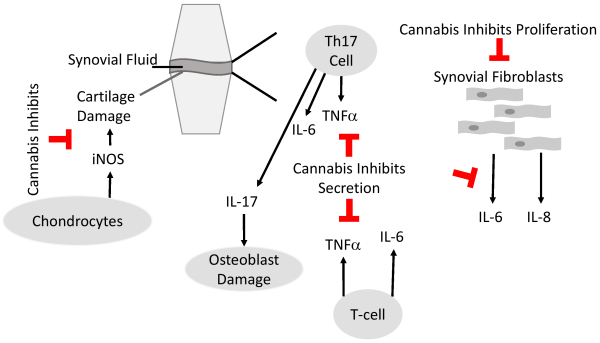
Figure 2.
Anti-arthritic Properties of Cannabinoids.
Scheme depicts the most important immune cells in the synovial fluid that contribute to the development of rheumatoid diseases and where cannabis has an anti-arthritic impact. Cannabis inhibits the proliferation of synovial fibroblasts, secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines from immune cells, and the secretion of nitric oxide synthases, such as inducible NO synthase (iNOS), from chondrocytes, which prevents cartilage damage.